EconomicsOnline Test
Consumption Analysis
Consumption Analysis
Congratulations - you have completed Consumption Analysis.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
Pick the odd one out
Luxuries | |
Comforts | |
Necessaries | |
Agricultural goods |
Question 2 |
Choice is always constrained or limited by the _____ of our resources.
Scarcity | |
Supply | |
Demand | |
Abundance |
Question 3 |
The chief exponent of the Cardinal utility approach was
J.R.Hicks | |
R.G.D.Allen | |
Marshall | |
Stigler |
Question 4 |
Marginal Utility is measured by using the formula of
a
TUn-TUn-1 | |
TUn-TUn+1 | |
TUn+TUn+1 | |
TUn-TUn+1 |
Question 5 |
When marginal utility reaches zero, the total utility will be
Minimum | |
Maximum | |
Zero | |
Negative |
Question 6 |
Gossen’s first law is known as.
Law of equi-marginal utility | |
Law of diminishing marginal utility | |
Law of demand. | |
Law of Diminishing returns.
|
Question 7 |
The basis for the law of demand is related to
Law of diminishing marginal utility | |
Law of supply | |
Law of equi-marginal utility. | |
Gossen’s Law |
Question 8 |
The concept of consumer’s surplus is associated with
Adam Smith | |
Marshall | |
Robbins | |
Ricardo |
Question 9 |
Given potential price is Rs.250 and the actual price is Rs.200. Find the consumer surplus
375 | |
175 | |
200 | |
50 |
Question 10 |
Indifference curve approach is based on
Ordinal approach | |
Cardinal approach | |
Subjective approach | |
Psychological approach |
Question 11 |
The concept of elasticity of demand was introduced by
Ferguson | |
Keynes | |
Adam Smith | |
Marshall |
Question 12 |
Increase in demand is caused by
Increase in tax | |
Higher subsidy | |
Increase in interest rate | |
decline in population |
Question 13 |
The movement on or along the given demand curve is known as____
Extension and contraction of demand | |
shifts in the demand. | |
increase and decrease in demand | |
all the above |
Question 14 |
In case of relatively more elastic demand the shape of the curve is
Horizontal | |
Vertical | |
Steeper | |
Flatter |
Question 15 |
A consumer is in equilibrium when marginal utilities from two goods are
Minimum | |
Maximum | |
Equal | |
Increasing |
Question 16 |
Indifference curve was first introduced by
Hicks | |
Allen | |
Keynes | |
Edgeworth |
Question 17 |
Elasticity of demand is equal to one indicates
Unitary Elastic Demand | |
Perfectly Elastic Demand | |
Perfectly Inelastic Demand | |
Relatively Elastic Demand |
Question 18 |
The locus of the points which gives same level of satisfaction is associated with
Indifference Curves | |
Cardinal Analysis | |
Law of Demand | |
Law of Supply |
Question 19 |
Ordinal Utility can be measured by
Ranking | |
Numbering | |
Wording | |
None of these |
Question 20 |
The indifference curve are
vertical | |
horizontal | |
positive sloped | |
Negatively sloped |
Question 21 |
Utility analysis was developed by __________
Alfred Marshall and Adam Smith | |
Alfred Marshall and Prof. J.R.Hicks | |
Alfred Marshall and A.C.Pigou | |
Alfred Marshall and J.k.Easthan |
Question 22 |
According to the law of diminishing marginal utility, the utility from the consumption of each additional unit starts ____________
Increasing | |
Diminishing | |
Multiplying | |
None of these |
Question 23 |
Equi – Marginal Utility means equal marginal utilities derived from the consumption of more than ____________
Four Goods | |
Three Goods | |
Two Goods | |
One Good |
Question 24 |
The Concept of consumers surplus was introduced by ____________
Alfred Marshall | |
J.R.Hicks | |
A.C.Pigon | |
J.K.Easthan |
Question 25 |
The Indifference curve analysis was presented by _____________
Alfred Marshall | |
J.R.Hicks | |
A.C.Pigon | |
J.K.Easthan |
Question 26 |
The foundation for various other economic law is ________
Law of diminishing marginal utility | |
Law of equi-marginal utility | |
Consumer surplus | |
None of these |
Question 27 |
_________ is the other name given for Marshallian utility analysis
Total utility | |
Cardinal utility analysis | |
Marginal Utility | |
All of these |
Question 28 |
The ________ Principal is quite useful in explaining the “wather diamond paradox”
Equi-Marginal | |
Marginal Utility | |
Utility | |
Total Utility |
Question 29 |
Supply curve is _____________
An upward sloping curve | |
A downward sloping curve | |
A horizontal straight line | |
A vertical line |
Question 30 |
____________ of the following constitute ‘demand’ in economics
A desire to buy | |
A decision to buy | |
The purchasing power | |
All the above |
Question 31 |
Giffen’s goods are classified in to ____________ and ________ goods.
Superior | |
Inferior | |
Both ‘a’ and ‘b’ | |
None |
Question 32 |
The term ‘ceteris paribus’ means _____________
Speculation | |
Other things remaining constant | |
Veblen effect | |
Antoine Augustin cournot |
Question 33 |
There are ________ kinds of price elasticity of demand
Two | |
Three | |
Four | |
Five |
Question 34 |
A change in the quantity supplied is response to a change in the prince is called __________
Elasticity of supply | |
Elasticity of demand | |
Concept of Elasticity | |
Unitary Elastic of supply |
Question 35 |
Human wants have the capacity to get satisfied only ___________
Temporarily | |
Wants | |
Comforts | |
None of these |
Question 36 |
In Marshallian analysis, it is assumed that utility can be measured quantitatively in terms of units these units are called.
Utils | |
Utility | |
Luxuries | |
Comforts |
Question 37 |
___________ Is a powerful factor that influence demand.
Expense | |
Price | |
Income | |
Commodity |
Question 38 |
_____________ does P.x denotes.
Demand of a commodity | |
Quantity of the demand | |
Price of a commodity | |
All the above |
Question 39 |
Law of diminishing Marginal Utility assumes the marginal utility of money to be _________
Increasing | |
Decreasing | |
Constant | |
None of these |
Question 40 |
If the co-efficient elasticity is equal to zero represents __________ supply.
Perfectly elastic | |
Unitary inelastic | |
Relatively elastic | |
Perfectly inclastic |
Question 41 |
Higher Indifference curve indicates _____________
Higher level of satisfaction | |
Higher cost | |
Lower cost | |
Lower level of satisfaction |
Question 42 |
The Point of intersection of demand and supply curves is known as
Equilibrium | |
Disequilibrium | |
Partially Equilibrium | |
General equilibrium |
Question 43 |
Human wants are classified in to
Necessaries and Laxuries | |
Luxuries and comforts | |
Neccessaries and comforts | |
Necessaries and Luxuries |
Question 44 |
The Segment of a demand curve between two points is called
Straight Line | |
Point | |
Arc | |
Percentage |
Question 45 |
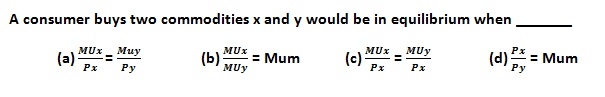
A | |
B | |
C | |
D |
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
There are 45 questions to complete.
This tests are helping me so well, please do create online test like this for 11th Commerce, Business Mathematics and Accountancy. This will help students for get full marks in one marks questions. Thank You.